Company Now To Move More Aggressively Into Electric Cars
Toyota, the king of hybrid vehicles, which has insisted that hydrogen fuel cells are the best zero-emission vehicle technology, is turning to batteries. The Japanese newspaper Chunichi Shimbun reports that the automaker is developing solid-state batteries for its future electric cars. The first vehicles to use that next-generation technology, the paper says without reporting sources, will go on sale early in 2022 in Japan—built on an entirely new platform.
This new type of battery would significantly increase electric driving range and reduce recharging time, removing the two key shortcomings associated with the lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles (EVs) today. Current mass market EVs typically have a range of only 125-to-250 miles and take 20-to-30 minutes to recharge even with fast chargers (several hours using conventional chargers).
Solid-state batteries are predicted to have a driving range of 200-to-300 miles, depending on battery size, and take just minutes to recharge.
What’s A Solid-State Battery?
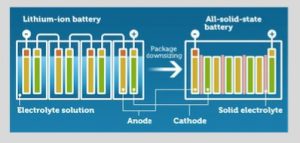
A solid-state battery uses a solid electrolyte between the cathode and anode; it needs only small separators between each cell. Conventional lithium-ion batteries use a liquid electrolyte that requires large spacers. Replacing the flammable liquid electrolyte found in today’s lithium-ion batteries eliminates the risk of fire and explosion associated with current battery technology. That danger, while low, remains a concern for many people considering the purchase of an electric car.
That also means that solid-state batteries do not require the use of sophisticated cooling systems to stabilize the temperature inside battery packs. Those battery management systems add cost, weight and bulk to an electric car. Solid-state batteries will not need such elaborate cooling systems, which should help bring down the cost of building an electric car. Also, solid state-batteries are smaller and weighs less, which adds to the appeal.
Toyota Not Anti-Battery Monster
Toyota has been taken to task by the media for what they see as a disinterest in battery electric vehicles. Nothing could be farther from the truth, even though at present the company does not offer a pure EV (it does have the plug-in hybrid Prius Prime).

No other automaker comes close to placing large quantities of batteries into vehicles. Since Toyota started producing hybrid vehicles in 1997, the company has put 10.7 million batteries on the road through June 2017. From that fact alone, one should concede that Toyota knows a thing or two about batteries.
Add to that, Toyota has also been working on advanced batteries for years as well. In 2008, the automaker set up its battery research division at its Higashi-Fuji Technical Center in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan, after sounding out battery manufacturers on whether they could develop all solid-state and lithium-air batteries. The automaker was told that it would be extremely difficult, so it decided to develop its own.
Toyota president Akio Toyoda created a new partnership last year that combined engineers from Toyota Industries Corporation, Denso Corporation, Aisin Seiki Company and Toyota Motor Company (all part of the Toyota keiretsu, a group of companies with interlocking business relationships and shareholdings) to design an electric car. The goal is to produce quick results.
Like all major carmakers, Toyota has its eye on China’s booming auto market. It plans to introduce an electrified version of its C-HR small crossover SUV using conventional lithium-ion batteries in 2019. This is prompted by the Chinese government’s instance that at least 10 percent of new vehicles sold in the country be EVs.
Solid-State Battery Race Is On
Toyota appears to be close to introducing a solid-state battery to power electrified vehicles in the next five years, but they are not alone. Dozens of other companies, including BMW and Hyundai, along with battery manufacturers and start-ups, are pouring billions of dollars of research and development funding into solid state batteries. Whoever comes to market first will leapfrog competitors and have a distinct advantage.
Will that company be Toyota? Only time will tell
Related Stories You Might Enjoy:
Road Test: 2017 Toyota Prius Prime
News: Toyota’s Future Vision—Concept-i
Tech: How Long Do Hybrid Batteries Last?
Tech: How Do Hybrid & Plug-in Hybrid Batteries Charge?

6 thoughts on “Tech: Toyota Going Electric with Solid-State Batteries”